(Revenue Regulations No. 11-2025 published on February 27, 2025)
This Tax Alert is issued to inform taxpayers regarding the implementation of the issuance of electronic invoices and electronic sales reporting under Sections 237 and 237-A of the National Internal Revenue Code (Tax Code) of 1997, as amended by Republic Act No. 12066 or CREATE MORE Act.
A. Definition of Terms
1. Electronic Invoice shall refer to a written account evidencing the sale, exchange or transfer of goods, properties, services, and/or lease/use of properties, issued in the ordinary course of trade or business, using an accounting/invoicing software or system with invoice management tools that is registered/accredited with the BIR containing the vital information as prescribed in the existing rules and regulations. It is a system-generated invoice issued to the buyers in a digital/electronic format (e.g., via email as Portable Document Format (PDF) attachments or email content or through electronic viewing in mobile or system application) or subsequently printed which can be easily extracted and transmitted electronically to the BIR for electronic sales reporting.
Note that a photo or scanned copy (in any file format) of a paper invoice (physical/manual copy) does not qualify as an electronic invoice.
Invoices generated by a CAS, and CBA with Accounting Records (with electronic invoicing), Cash Register Machines (CRM), POS System, or other invoicing software and subsequently printed on paper for issuance to buyers, without the capability or readiness to electronically report the sales and invoice data, shall not qualify as electronic invoices. Instead, they shall be classified as traditional, manually issued invoices.
2. Electronic Invoicing – refers to the automated process of generating an electronic invoice in a structured invoice data which can be easily extracted electronically from the invoice allowing for automated electronic data processing.
3. Electronic Sales Reporting System (ESRS) – refers to the electronic reporting or process of storing, transmitting, and/or receiving the electronic invoice data, through direct system-to-system data transfer without manual entry, to the BIR in a structured electronic format (e.g. (e.g., JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) file format or Extensible Markup Language (XML) and such other format as may be prescribed by the BIR). The electronic invoice data contains sales information from sellers to buyers and may also contain payment information made by the buyers.
4. Electronic Commerce (E-commerce) – refers to any commercial transaction (e.g. sale or offer of sale, purchase of physical or digital goods and services, or lease or offer for lease) conducted through electronic, optical, and similar medium, mode, instrumentality, and technology. These commercial transactions may be digitally ordered, digitally delivered, or platform-enable transactions.
5. Internet Transaction – refers to the sale or offer of sale, or lease or offer for lease, of digital or non-digital goods and services over the internet.
B. Compliance Deadlines
Under the transitory provisions of RR, taxpayers covered under Section 3 (A) (1) to (3) of the RR have a period of one (1) year from the effectivity date of the Regulations to comply with the electronic invoicing requirements (issuance of electronic invoice). Since the RR was published on 27 February 2025, it became effective on 14 March 2025. Hence, covered taxpayers have until 14 March 2026 to comply with the requirement to issue electronic invoices.
Upon the establishment of a system capable of storing and processing the required data by the BIR, all taxpayers covered under Sections 3 (A) (5) (i), 3 (A) (5) (ii), 3 (A) (5) (iii) and 3 (A) (5) (iv) and 3 (B) of the RR shall be mandated to comply with the issuance of electronic invoice and Electronic Sales Reporting System (ESRS) requirements. A separate Revenue Regulations shall be issued for this purpose.
C. Covered Taxpayers by Electronic Invoicing and ESRS
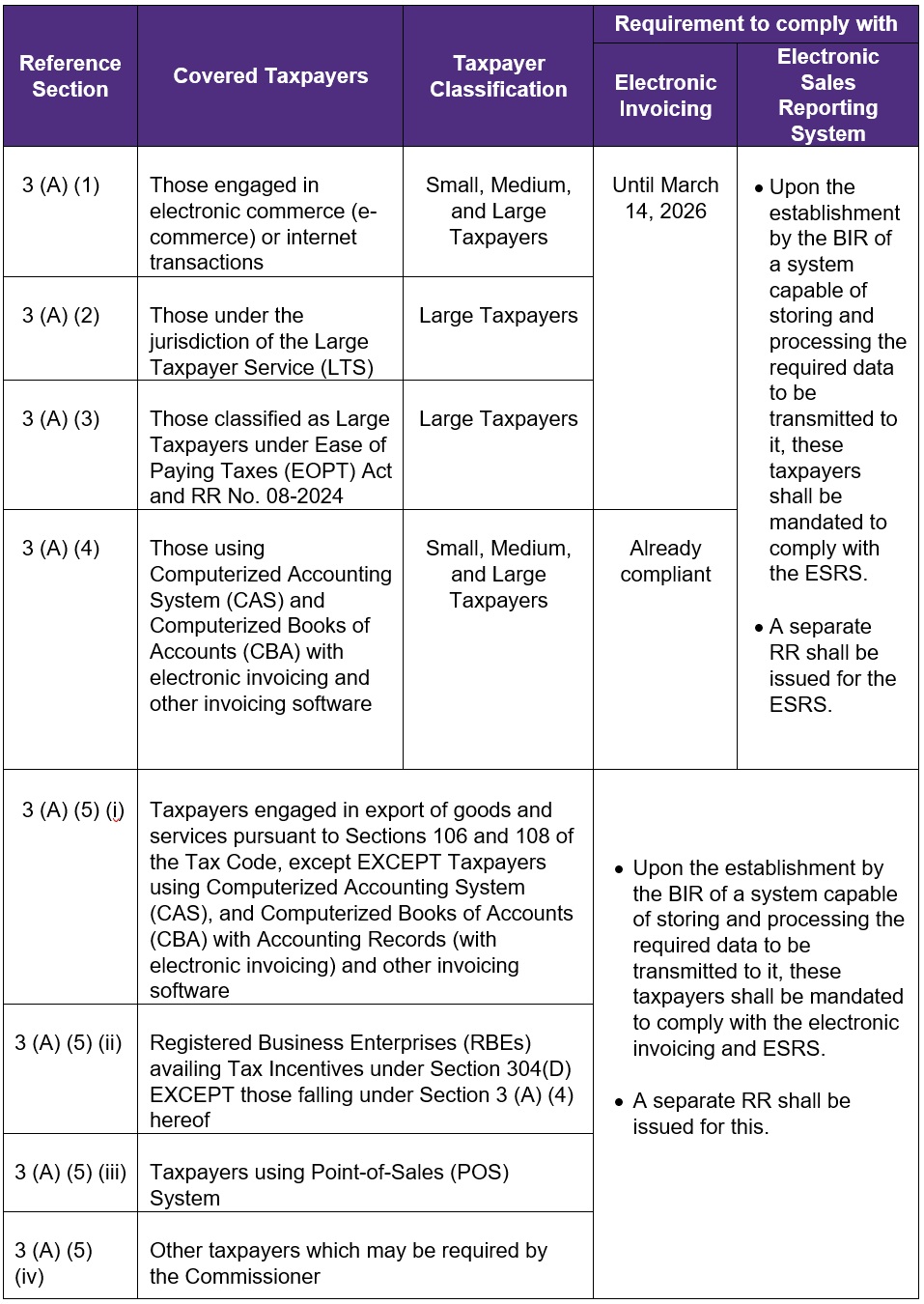
- In case the above taxpayers or business activities are registered to a Branch Office, the taxpayers' Head Office and all its Branch Offices shall also be covered by electronic invoicing and electronic sales reporting.
- Taxpayers engaged in e-commerce shall cover persons, whether natural or juridical, who are engaged in the following trade or business in the Philippines, including but not limited to:
a. E-commerce or online businesses, whether formal or informal, including sale, procurement, or availment of physical or digital goods (including virtual items in online games), digital content/products, digital financial services, entertainment services, social commerce, on-demand labor and repair services, and property and space rentals;
b. Operation of digital platforms, including e-marketplace platforms;
c. Sale and/or lease of goods and services through digital platforms;
d. Digital content creation and streaming that are income generating including online advertising, blogging/vlogging, subscription or commission;
e. E-retailing of goods and services;
f. Sale of creative or professional services, on-demand or freelance services or digital services supplied over the internet;
g. On-demand Services over the internet, available whenever a customer request them, rather than being provided on a fixed schedule such as, but not limited to, ride-sharing, food delivery, grocery delivery, home services (like cleaning or repairs), and streaming entertainment;
h. Transport and Delivery Services contracted through an online platform, application, website, webpage or other similar platform operated by the provider, regardless of whether the provider is authorized to engage in e-commerce in the Philippines; and
i. Other form of businesses other than those mentioned above which are conducted online.
- Micro Taxpayers are exempt from the mandatory requirement to use and issue electronic invoice but they may voluntarily use the same. In lieu of electronic invoices, Micro Taxpayers shall issue a registered manual invoice. They may also use CAS, CRM, and POS System, in lieu of electronic invoices.
D. Additional Allowable Deductions
All taxpayers that are mandated to issue electronic invoices and are covered by the electronic sales reporting system, including those who voluntarily complied both with the issuance of electronic invoice and electronically report their sales date to the BIR, shall be granted the following deduction from their taxable income:
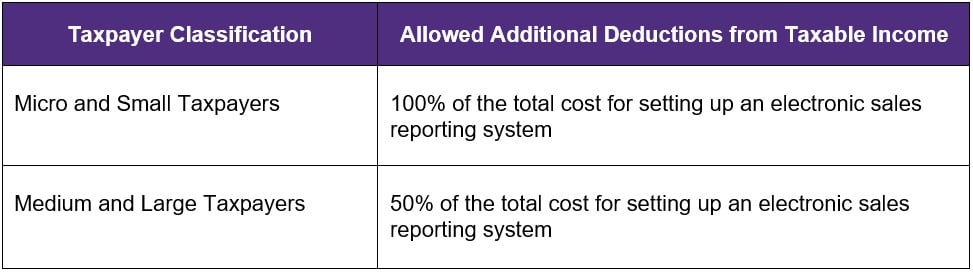
The additional deduction can be claimed only once within the taxable year in which the electronic sales reporting system has been completed, or the final payment has been made. Further, the importation of such system shall also be exempt from taxes.
E. Effectivity
The regulation shall take effect fifteen (15) days after its publication in the Official Gazette or the BIR Official Website. The regulation was published on the BIR Official Website on Thursday, February 27, 2025.

